Semiconductors: Artificial Intelligence is redesigning the map of what was once the symbol of globalization. However, the decoupling between China and United States could change the game.
The market for semiconductors: a brief analysis to better understand what could happen in the technological and global geopolitical spheres.
Nvidia’s superchip for artificial intelligence, the Gpu H100, is considered the most advanced in the world with its 80 billion transistors. Research centers such as the Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Los Alamos National Lab, and the University of Tsukuba will use it in their future supercomputers, as well as servers from major cloud computing providers like Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and Oracle.
However, the US government has banned the export of this accelerator to China, concerned about not giving Beijing a technological advantage and to prevent products from being used for military purposes in China and Russia.
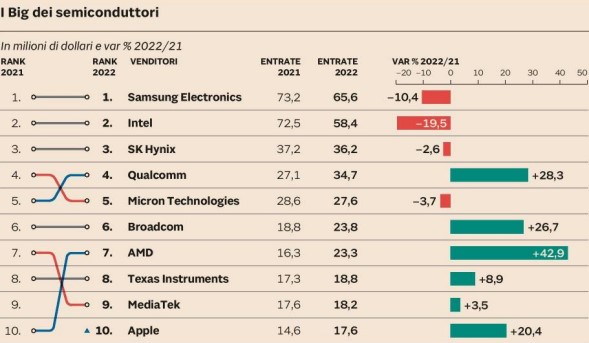
Credits Gartner / Il Sole 24 Ore
Future scenarios in global geopolitics
What consequences can we imagine? Analysts predict that chips will become the ground on which geopolitical balances will be redrawn. After the pandemic, which triggered the biggest semiconductor supply crisis in history, major powers are focused on building their own chip industry through technological decoupling, pushing major producers to pursue digital self-sufficiency.
Beijing, which is technologically less advanced than the United States in chip design but is also the world’s largest exporter of rare earths (the most valuable raw material for the electronics industry), is ready to launch a $143 billion plan to develop its own chip industry, triple that of the United States and quadruple that of Europe.
This technological self-sufficiency among different powers neither seems sustainable nor sensible: there is a risk of creating too wide a technological gap and making international collaboration on crucial issues such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity more difficult. In addition, dependence on a single country or region for chip supply could also pose a problem for national security and economic stability.
The chip industry has always been a cornerstone of globalization: today, one of the main problems that has led to the shortage of these products is the strong concentration of factories worldwide. There are few, and those capable of producing the most sophisticated microchips are only two: Tsmc in Taiwan and Samsung in South Korea.
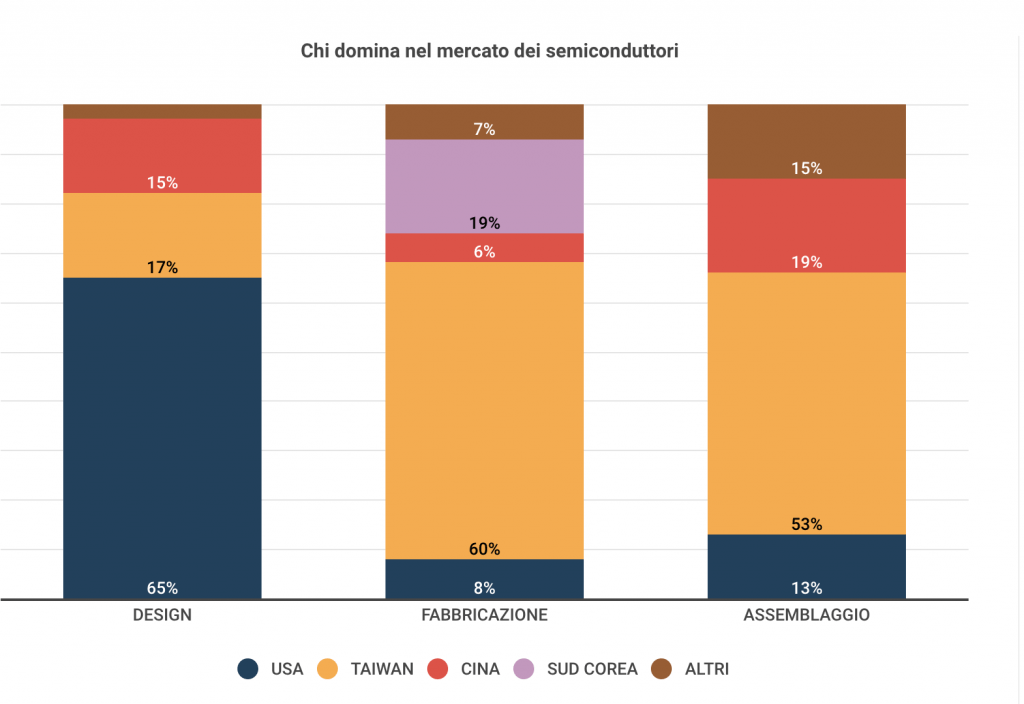
Credits: key4biz.it
It is easy to understand how the race for chips has now become a geopolitical and strategic issue of paramount importance, with significant consequences for the electronics industry, cybersecurity, and international relations. Their production is no longer just a technological issue, but also a political and economic one that requires an integrated approach and international collaboration: raising borders where there were none, as was done in the twentieth century, this time will not be so simple and could have too risky and difficult-to-predict consequences.
Maker Faire Rome – The European Edition, promoted by the Rome Chamber of Commerce, has been committed since its first edition to making innovation accessible and usable, offering content and information in a constantly updated blog full of opportunities for the curious, makers, SMEs, and companies that want to enrich their knowledge and expand their business, in Italy and abroad.
Follow us, subscribe to our newsletter: we will provide you only with the right information to deepen the topics of your interest.



















































































